백준 11559 Puyo Puyo
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/11559
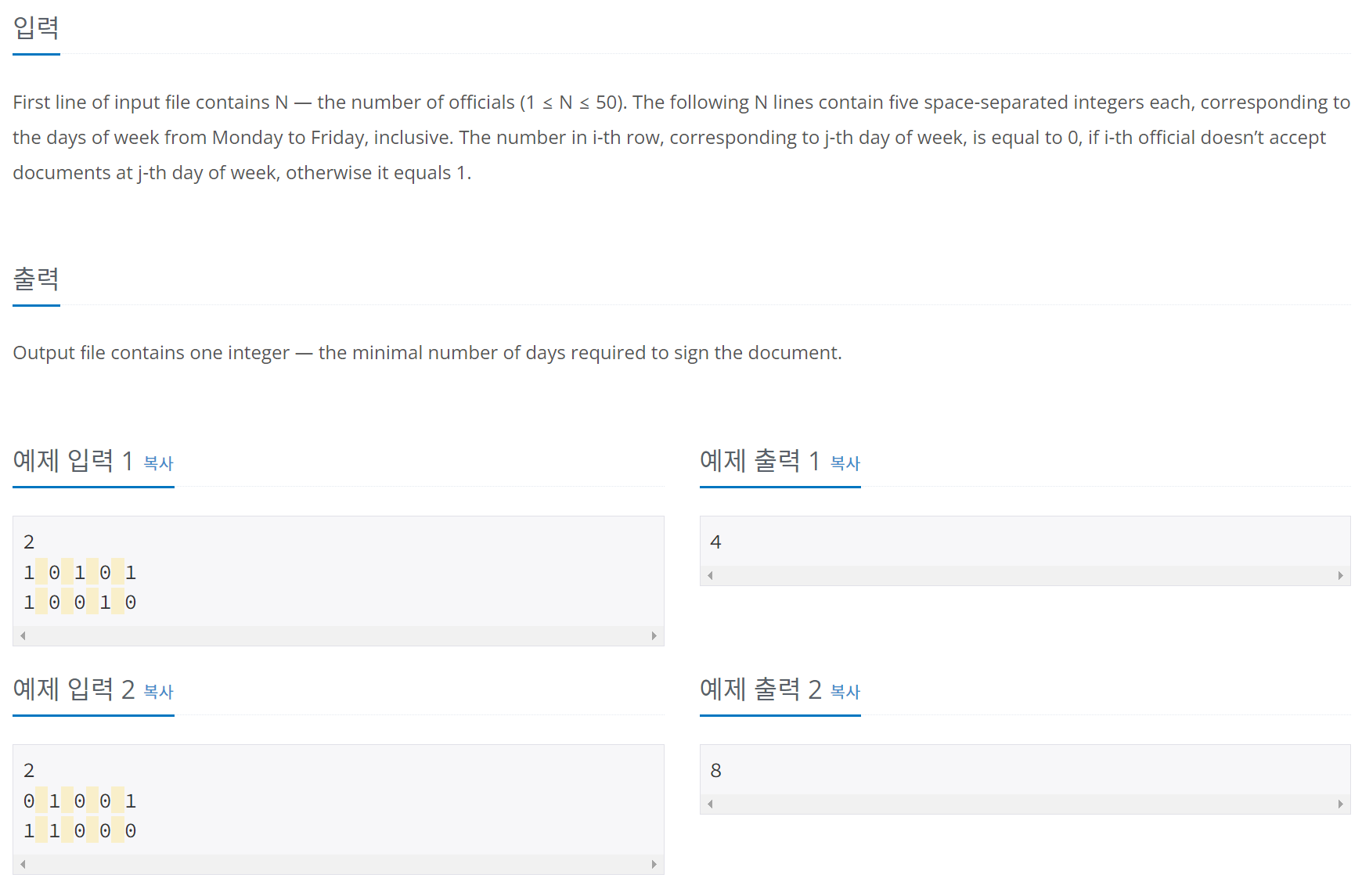
11559번: Puyo Puyo
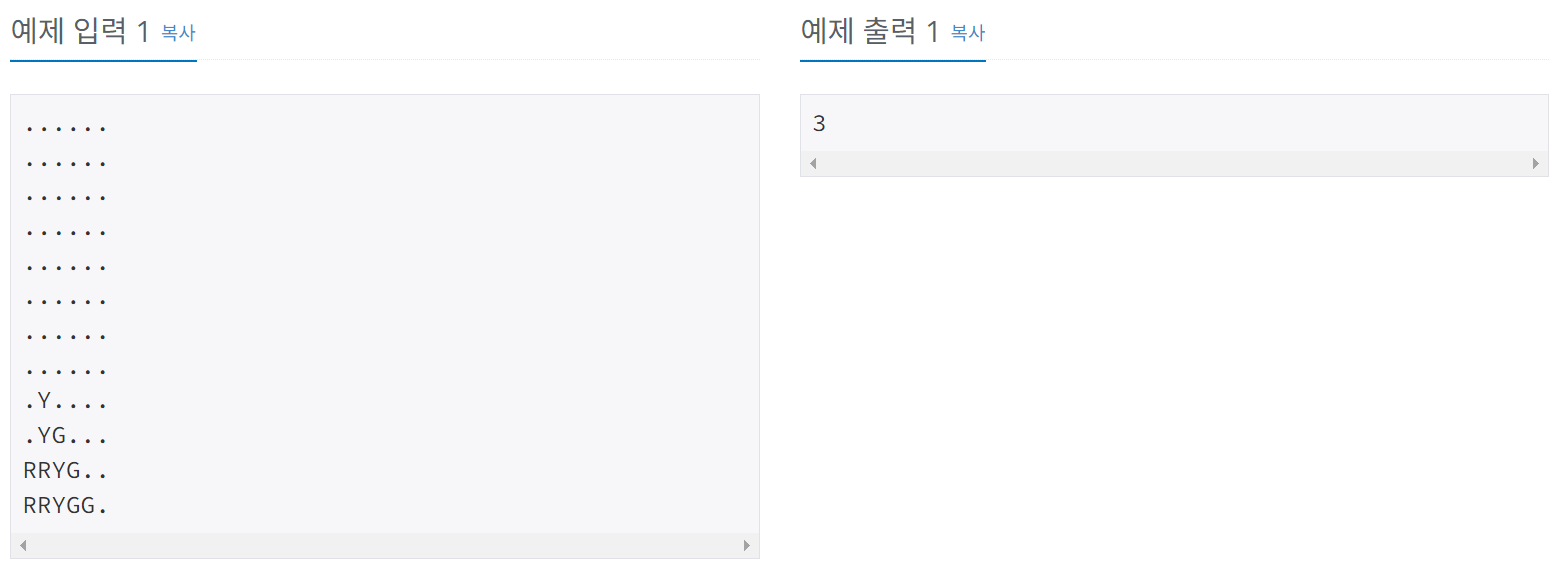
총 12개의 줄에 필드의 정보가 주어지며, 각 줄에는 6개의 문자가 있다. 이때 .은 빈공간이고 .이 아닌것은 각각의 색깔의 뿌요를 나타낸다. R은 빨강, G는 초록, B는 파랑, P는 보라, Y는 노랑이다.
www.acmicpc.net
Comment
기본적인 탐색 + 구현 시뮬레이션 문제
확실히 구현이 들어가니까 실수하는게 생기고 실수했을 때 원인찾기가 어렵다. 지금은 디버깅으로 가능하지만 코테에서는 신경을 많이 써서 해야할 듯?
Hint
- 기본적인 BFS이동을 담을 movePoint
- 방문체크 visited
- 게임판 puyoMap
- 연쇄횟수
- 매 라운드가 있어야하기에 puyoClear(boolean)
- 연쇄가 발생했을 때 뿌요를 지울 ArrayList
아직 깔끔하게 구현은 못하겠지만 어느걸 써야할지는 계속 생각하며 풀어야 함
Solution
1. 탐색하고 탐색된 좌표 저장
2. 탐색된 좌표가 4개 이상일 때 puyoClear = true, 실제로 지울 clearPuyoMap List에 추가
3. clearPuyoMap 기반으로 뿌요들을 아래로 내려줌
4. 한번 지워진 상태(puyoClear == true)라면 1~3 반복
큰 흐름은 위의 순서로 진행된다.
값 초기화 잘 신경써서 해주면 크게 어렵지는 않다.

1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 | package Baekjoon.gold; import java.io.*; import java.util.*; public class p11559 { static final int[][] movePoint = {{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}}; static boolean[][] visited = new boolean[12][6]; static char[][] puyoMap = new char[12][6]; static int count = 0; static int n = 12; static boolean puyoClear = false; static ArrayList<int[]> accumulatePuyoMap = new ArrayList<>(); static ArrayList<int[]> clearPuyoMap = new ArrayList<>(); public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { puyoMap[i] = br.readLine().toCharArray(); } do { puyoClear = false; puyoGame(); if (puyoClear) { count++; puyoMove(); } clearPuyoMap.clear(); visited = new boolean[12][6]; } while (puyoClear); System.out.println(count); } static void puyoGame() { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) { if (puyoMap[i][j] != '.' && !visited[i][j]) { bfs(i, j, puyoMap[i][j]); } } } } static void bfs(int x, int y, char puyoColor) { Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>(); visited[x][y] = true; q.add(new int[]{x, y}); accumulatePuyoMap.clear(); accumulatePuyoMap.add(new int[]{x, y}); while (!q.isEmpty()) { int[] nowXY = q.poll(); for (int[] moveXY : movePoint) { int nowX = nowXY[0] + moveXY[0]; int nowY = nowXY[1] + moveXY[1]; if (nowX >= 0 && nowY >= 0 && nowX < 12 && nowY < 6 && puyoColor == puyoMap[nowX][nowY] && !visited[nowX][nowY]) { visited[nowX][nowY] = true; q.add(new int[]{nowX, nowY}); accumulatePuyoMap.add(new int[]{nowX, nowY}); } } } if (accumulatePuyoMap.size() >= 4) { puyoClear = true; clearPuyoMap.addAll(accumulatePuyoMap); } } static void puyoMove() { //4개 이상인 뿌요를 .으로 초기화 for (int[] clearXY : clearPuyoMap) { puyoMap[clearXY[0]][clearXY[1]] = '.'; } //.을 탐색하며 뿌요를 위로 올려줌 int[] firstDotPlace = new int[2]; for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) { boolean firstDotCheck = false; Queue<Character> upMovePuyo = new LinkedList<>(); for (int j = 11; j >= 0; j--) { if (puyoMap[j][i] == '.') { if (firstDotCheck) { continue; } firstDotPlace[0] = j; firstDotPlace[1] = i; firstDotCheck = true; } else if (firstDotCheck) { upMovePuyo.add(puyoMap[j][i]); puyoMap[j][i] = '.'; } } int nowX = firstDotPlace[0]; int nowY = firstDotPlace[1]; while (!upMovePuyo.isEmpty()) { puyoMap[nowX][nowY] = upMovePuyo.poll(); nowX--; } } } } | cs |
'공부 > Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 16401 과자 나눠주기 자바로 풀어 본 짧은 글 (0) | 2023.12.02 |
|---|---|
| 백준 29812번 아니 이게 왜 안돼 자바로 풀어 본 짧은 글 (0) | 2023.12.01 |
| 백준 2310번 어드벤처 게임 자바로 풀어 본 짧은 글 (0) | 2023.11.28 |
| 백준 12755번 수면 장애 자바로 풀어 본 짧은 글 (0) | 2023.11.21 |
| 백준 14494번 다이나믹이 뭐예요? 자바로 풀어 본 짧은 글 (0) | 2023.09.15 |